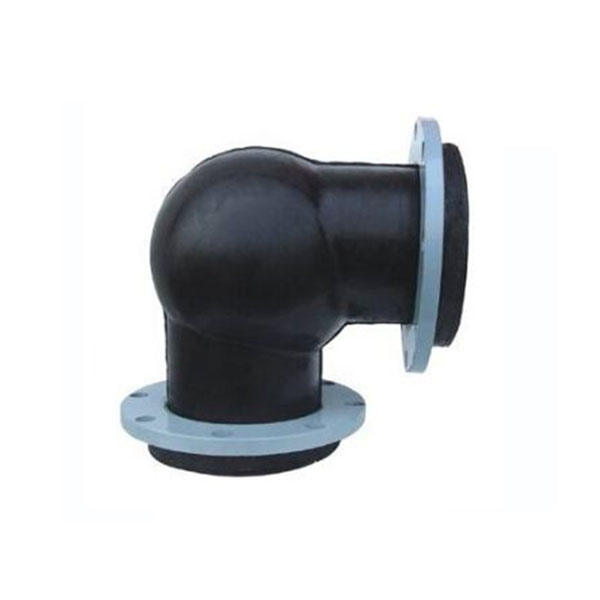
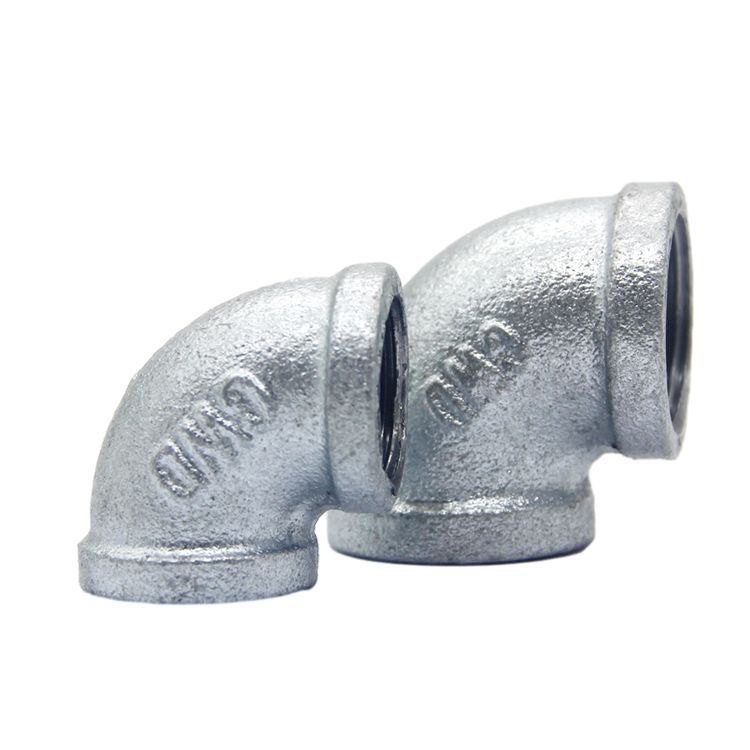
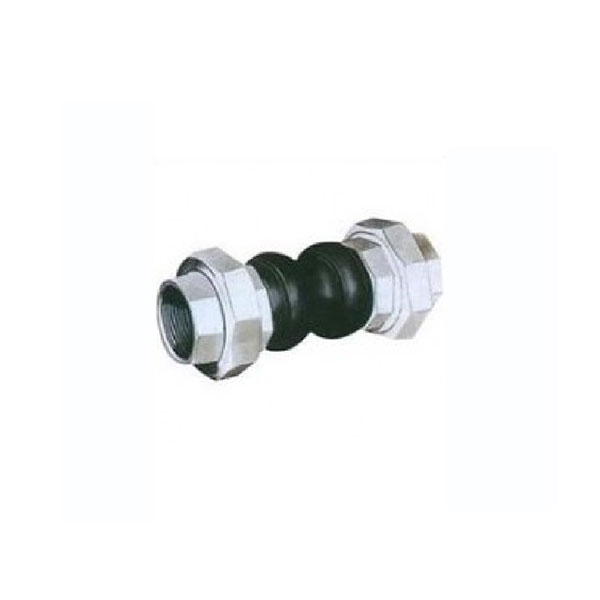
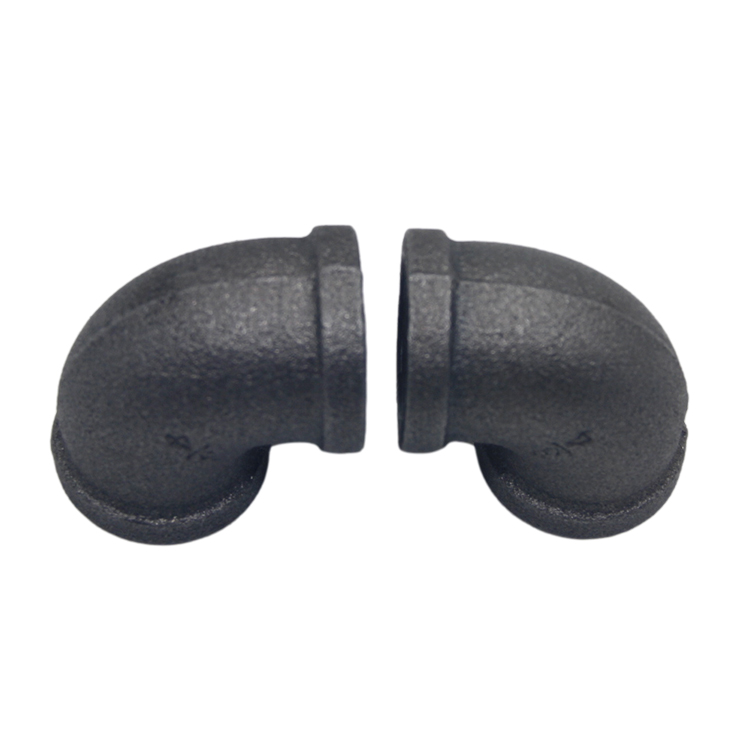
Elbow Type Rubber soft joint
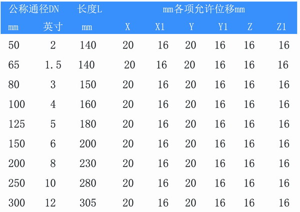
Specifications
Product Introduction
Each structure can be divided into three types according to its shape:
1.Concentric diameter: The inner diameter and outer diameter of the expansion joint are the same, forming a concentric shape.
2.Concentric reduction: The inner diameter and outer diameter of the expansion joint are different, forming a cone shape.
3.Eccentric reducing: the inner diameter and outer diameter of the expansion joint are different, and the center line of the joint is not aligned, forming an eccentric shape.
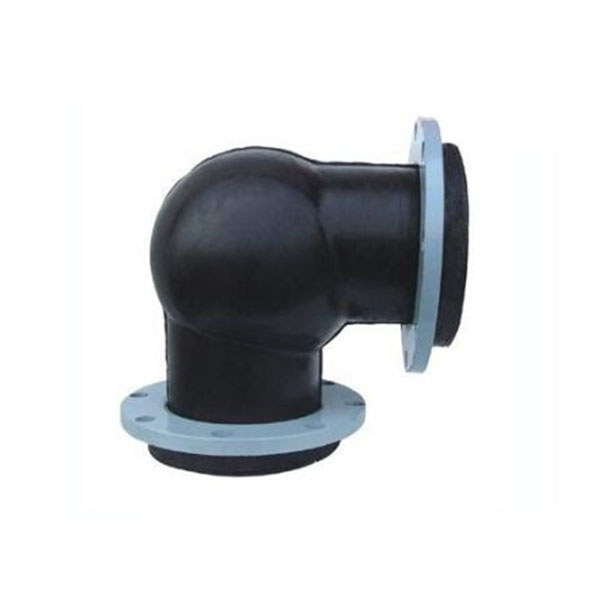

Connection form: The rubber expansion joint can be connected with the pipeline in different ways according to the specific use and requirements. Connection forms include:
1.Flange connection: both ends of the expansion joint with flanges, using bolts and pipe connection, safe and reliable connection.
2.Threaded connection: Both ends of the expansion joint are threaded and can be threaded with the pipe.
3.Clamp connection: The expansion joint can be clamped to the pipe using a hose clamp or other similar mechanism for quick and easy installation.
4.Threaded pipe flange connection: This type of connection combines threaded and flanged connections to provide versatility in mounting options.
Working pressure level: The rubber expansion joint has different working pressure levels to adapt to different system requirements and operating conditions. Working pressure levels are usually expressed in megapascals (MPa) and include various levels:
0.25 MPa/0.6 mpa/1.0 MPa/1.6 mpa/2.5 mpa/6.4 mpa
Other factors to consider when selecting the correct operating pressure level include the type of fluid being conveyed, the flow rate required, and the potential for future system expansion or modification. Potential consequences of exceeding operating pressure levels, such as system leaks, component failure, or safety hazards, must also be considered. Regular inspection and maintenance should be performed to monitor the performance of the system and ensure that the selected operating pressure level remains appropriate over time.







